What is RFID technology?
RFID systems consist of a transponder (RFID tag) and a reader. When the transponder comes within range of the reader, it transmits a unique identification number to the reader via radio waves. The reader forwards this data to software that processes the information and performs authentication or registration. The RFID transponder is usually an RFID tag or an RFID chip card with a unique identification number. The RFID reader generates the electromagnetic field and transmits the data. Depending on the design, different protocols and interfaces are used.
Examples of RFID technology applications
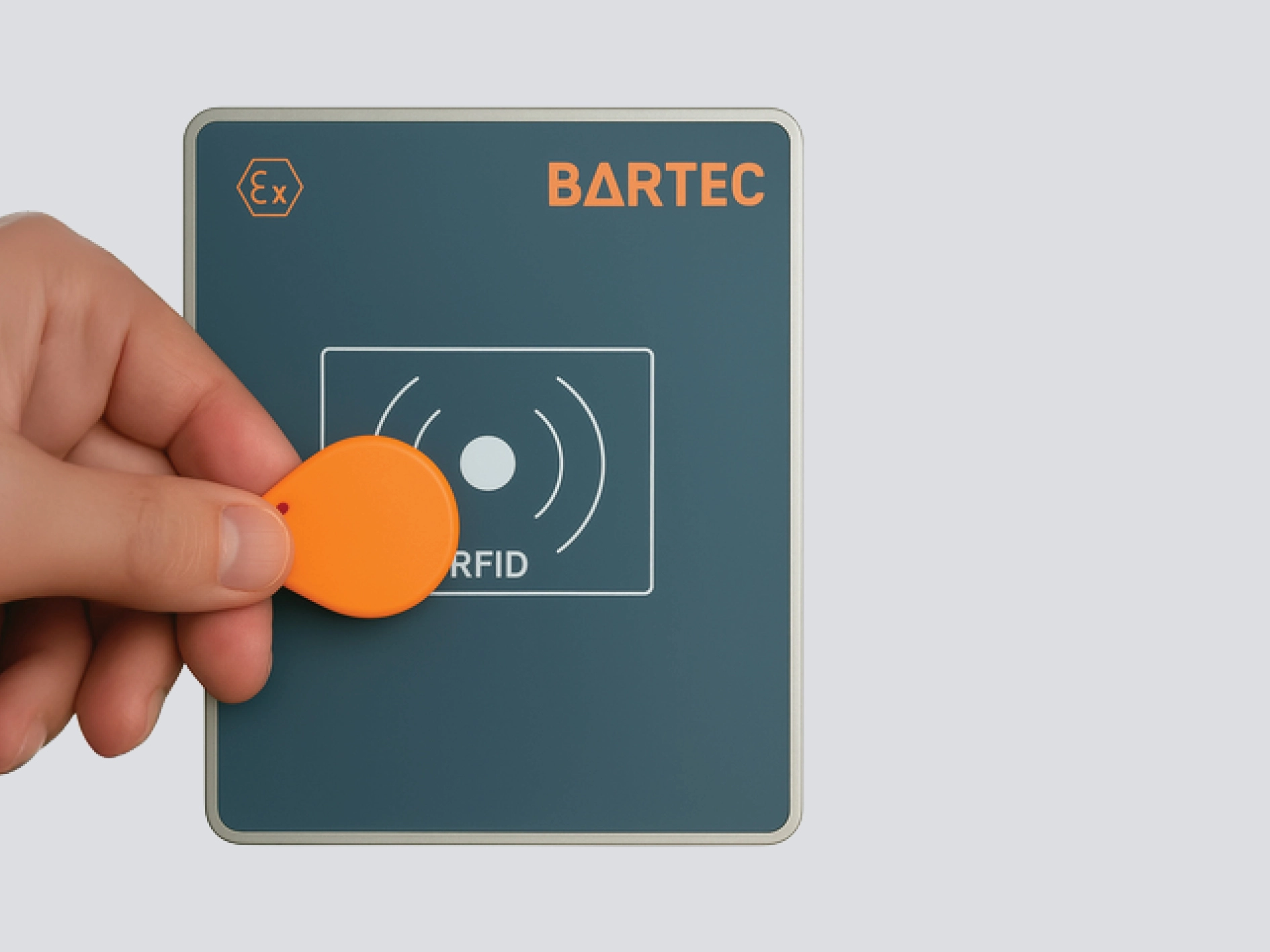

RFID access control enables regulated access to buildings, rooms, or server systems, replacing manual password entry or the use of physical keys with modern, electronic methods. RFID can also be used for the authorization and management of machines or management systems – for example, for activating charging stations, refueling vehicles, or registering and operating control systems. In the process industry, user authentication at operator stations (e.g., thin clients) allows employees to log in quickly and easily using an RFID card, thus ensuring secure identification.
Compliance of RFID systems with FDA requirements
RFID user authentication can meet the requirements of FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulation 21 CFR Part 11, provided certain technical and procedural controls are implemented. The regulation explicitly permits various authentication methods, such as RFID, as long as they ensure the required level of security. It is important that RFID systems listed within the system in use are employed.
RFID Technology for IT security
In the context of digital transformation, security concepts against cyberattacks are one of the most important tasks for IT experts. This task has already been addressed in most companies, as RFID systems for access control or user authentication are now almost ubiquitous.
Nevertheless, many companies are hesitant to use these systems in hazardous areas (Ex zones) because the currently deployed hardware is not available for such environments. This raises the question: How can the hardware "approved" by IT or the manufacturer of the process control system also be used in hazardous areas?
RFID readers in hazardous areas
BARTEC's portfolio for potentially explosive atmospheres encompasses a wide range of product variants to allow maximum flexibility in the choice of material quality, dimensions, and connection methods for diverse requirements worldwide. These solutions enable the use of the same equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres that users employ in their safe zones.
The MODEX RFID solution for Zone 1/21
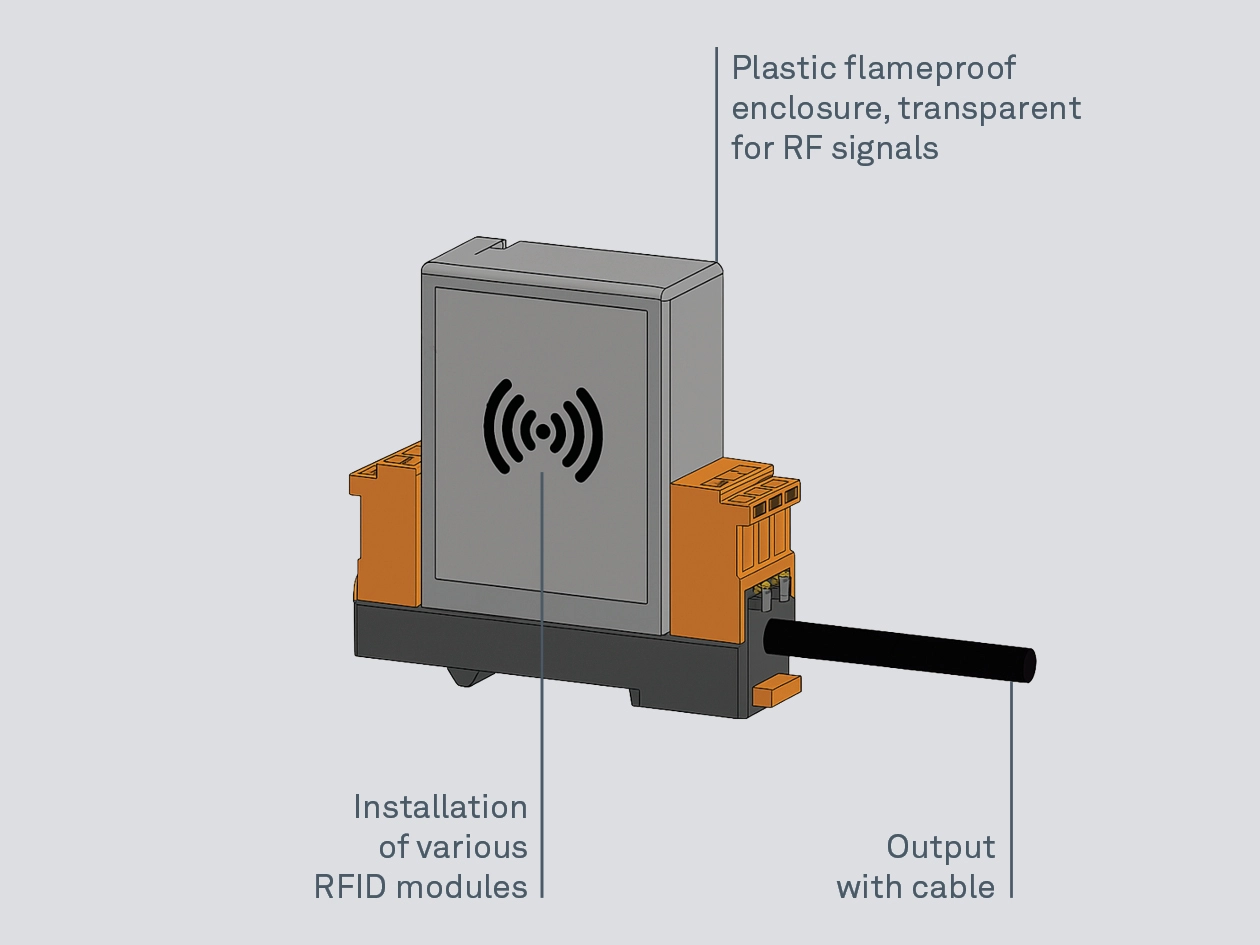
The MODEX RFID enclosure is based on the "Ex d" type of explosion protection. The "Ex d" type of protection works by containing any explosion that might occur inside the enclosure. This is achieved through an explosion-pressure-resistant enclosure design combined with flameproof gaps at all enclosure openings. The "MODEX" (Modular Explosion Protection) concept is simple and has proven itself in the market for decades.
Instead of heavy aluminum housings, plastic housings are used. By reducing the internal air volume through the filling material, the housings can be designed and built to be lightweight and compact, while still meeting the requirements of the Ex d type of protection for explosive atmospheres.
The electrical connection is made via a data cable (no terminals are required), and installation in an Ex e enclosure is unnecessary. Mechanical protection is entirely sufficient. This protection is achieved by the GMP-compliant front panel.
The MODEX RFID enclosure allows for the easy installation of most common RFID modules, such as those from Siemens, rf -IDEAS, PHG, or HID-Global, in potentially explosive atmospheres. Thanks to its plastic housing, radio signals are not disrupted, enabling the use of standard RFID technology systems even in explosion-proof areas. For GMP-compliant installation, the MODEX RFID enclosure is mounted behind a BARTEC RF front cover. The RF front cover is designed for front panel mounting. For applications within an approved Ex e enclosure, the BARTEC enclosure window is available.
Digital solutions for explosive atmospheres
BARTEC and its brand Extronics, which specializes in the development and manufacturing of connectivity and IIoT infrastructure as well as systems for plant and personnel tracking, have developed various enclosure concepts that cover almost all applications facing the challenges of digital transformation. For the use of non- explosion-proof communication devices, such as RFID technology systems, access points, or gateways, various enclosure concepts are available for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.
With the right concepts, RFID technology systems can be implemented easily and without concern even in explosive areas. The use of certified hardware components ensures IT security and seamless integration into existing system landscapes. BARTEC's flexible enclosure concepts allow for the reliable and standards-compliant deployment of a wide range of hardware solutions – from communication modules to IIoT components – even in hazardous areas.


